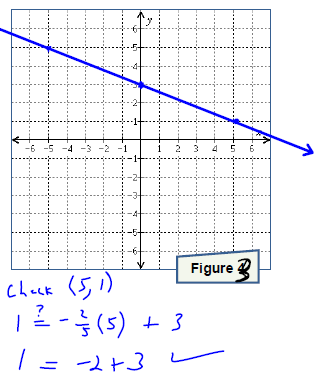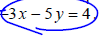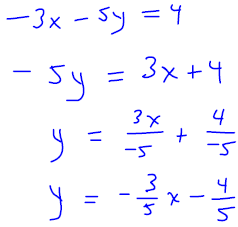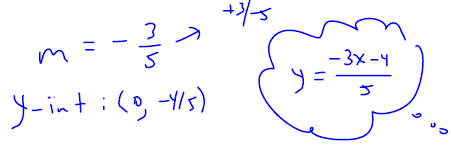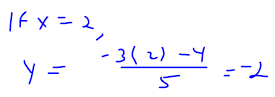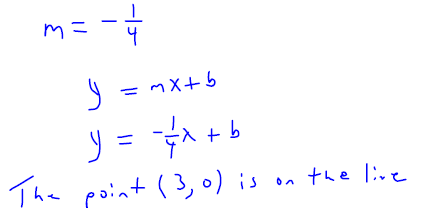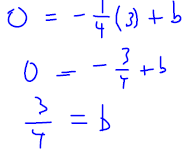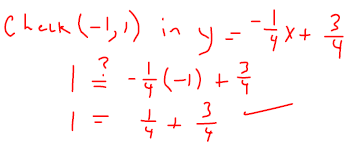|
Home Graphing and Writing Linear Functions SOLVING EQUATIONS INVOLVING RATIONAL EXPONENTS Linear Equations and Graphing Systems of Linear Equations Solving Polynomial Equations Matrix Equations and Solving Systems of Linear Equations Introduction Part II and Solving Equations Linear Algebra Graphing Linear Inequalities Using Augmented Matrices to Solve Systems of Linear Equations Solving Linear Inequalities Solution of the Equations Linear Equations Annotated Bibliography of Linear Algebra Books Write Linear Equations in Standard Form Graphing Linear Inequalities Introduction to Linear Algebra for Engineers Solving Quadratic Equations THE HISTORY OF SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATIONS Systems of Linear Equations Review for First Order Differential Equations Systems of Nonlinear Equations & their solutions LINEAR LEAST SQUARES FIT MAPPING METHOD FOR INFORMATION RETRIEVAL FROM NATURAL LANGUAGE TEXTS Quadratic Equations Syllabus for Differential Equations and Linear Alg Linear Equations and Matrices Solving Linear Equations Slope-intercept form of the equation Linear Equations DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS QUADRATIC EQUATIONS Linear Equation Problems Systems of Differential Equations Linear Algebra Syllabus Quadratic Equations and Problem Solving LinearEquations The Slope-Intercept Form of the Equation Final Exam for Matrices and Linear Equations Linear Equations |
Slope-intercept form of the equationKey Concepts: Slope-intercept form of the equation
of a line
Example 2
Definition and most awesome fact Example 3
Example 4
Example 5
Example 6
Example 7
Example 8
Example 9
Example 10
Example 11
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||


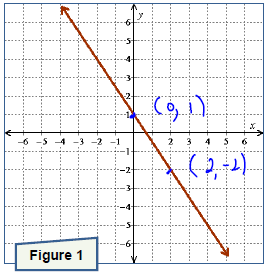
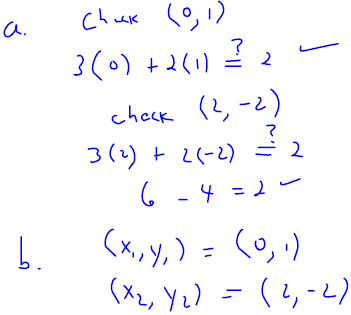
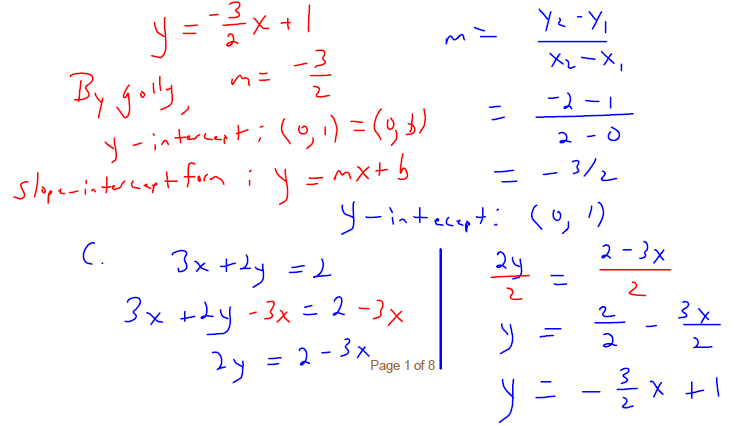
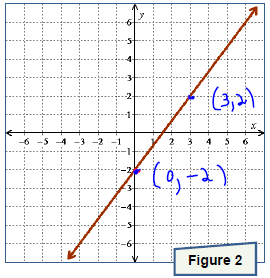
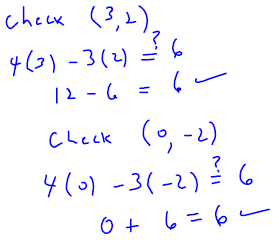
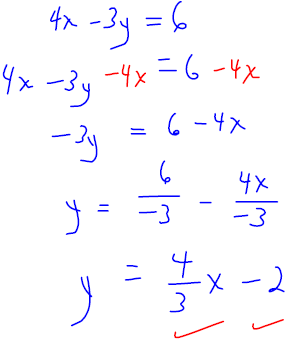
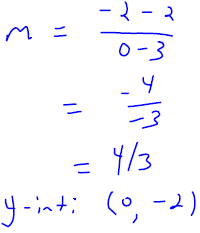
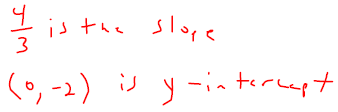
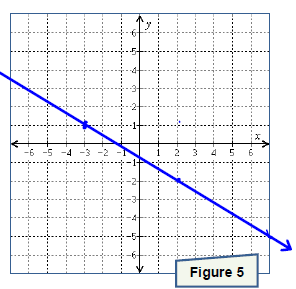
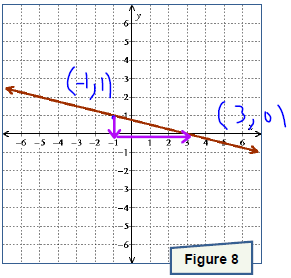
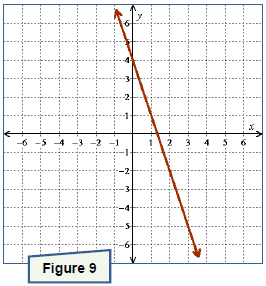
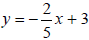 . Graph the line onto Figure 3.
. Graph the line onto Figure 3.